Windows 3.1 For Workgroups
It’s been 25 years since Microsoft released Windows for Workgroups 3.11. To take a trip back to the end of the 16-bit era of operating system, [Yeo Kheng Meng] got WFW 3.11 running on a modern Thinkpad.
Hlp to pdf online converter. To make things difficult, a few goals were set for the project. Obviously, this wouldn’t be much fun in a virtual machine, so those were banned. A video driver would be needed, since WFW 3.11 only supports resolutions up to 640×480 in software. Some basic support for sound would be desirable. Finally, TCP/IP networking is possible in WFW 3.11, so networking hardware would allow access modern internet.
Windows 3.1x Software. CAL3101P.ZIP, 613K: Calmira 3.101 German. Calmira is a Win95 style GUI including Start Menu, Taskbar, Explorer, and anything else a Win95 user might miss in Windows 3.1. Calmira can be configured individually and you may even become addicted to it;) And now for the best: Calmira is Open Source! Windows 3.1x and Windows For Workgroups was released between March 1992 and November 2003. The Windows 3.1x release spanned four releases and marked the end of the Home user Windows 3 line as well as the end of the 16-bit kernel. The build-in network feature made user easier to access and configure network inside Windows on the fly. But, Windows for Workgroups 3.xx does not support Internet dial-up network, it needs third-party software that often conflict with its own network feature. Nov 21, 2016 Windows 3.11 for workgroups came on several 1.44 MB floppies. Windows 95C is the first version of Windows to ship on CD media. In addition to Windows 3.11, you will also need to prepare a floppy disk. This will be hard to setup, you will probably need to use the original Virtual PC and use XP to create the virtual machine. For starters, set up Windows for Workgroups Networking with a NDIS driver and Netbeui. See Windows for Workgroups. As Trumpet Winsocks expects a packet driver interface, you need to install a shim: a driver that can communicate with the NDIS driver of your network card on one hand, and behaves as a packet driver on the other hand.
[Yeo Kheng Meng] accomplished all of these goals on a 2009 Thinkpad T400 and throughly documented the process. Some interesting hacks were required, including the design of a custom parallel port sound card based on the Covox Speech Thing. Accessing HTTPS web servers required a man-in-the-middle attack to strip SSL, since the SSL support on WFW 3.11 is ancient and blocked by most web servers today.
If you want your own WFW 3.11 laptop, the detailed instructions will get you there. [Yeo Kheng Meng] has also provided the hardware design for the sound card. You can watch a talk on the process after the break.
Home > Articles > Home & Office Computing > Microsoft Windows Vista & Home Server
␡- Windows 3.0, 3.1, and Windows for Workgroups
Windows 3.0
The third time was a charm. Windows 3.0, released in 1990, was the first commercially successful version of the operating system, selling 10 million copies in the two years before the 3.1 upgrade. This was the first version of the operating system to incorporate true multitasking, thus providing a real alternative to the dominant DOS operating system of the time. After the success of Apple's Macintosh, the PC world was ready for a multitasking OS with a graphical user interface.
Figure 4 Windows 3.0—the version that put Windows on the map
It helped, of course, that Windows 3.0 was a big improvement over the previous version. The interface was a lot nicer looking with 3D buttons and such, and users could, for the first time, change the color of the underlying desktop. (No wallpaper yet, however.) Programs were launched via the new icon-based Program Manager, and a new File Manager replaced the old MS-DOS Executive for basic file management. This was also the first version of Windows to come with Solitaire built in, contributing to an incredible amount of wasted time worldwide. Equally important, Windows 3.0 included a Protected/Enhanced mode that enabled native Windows applications to make use of more memory than their DOS counterparts.
After the release of Windows 3.0, applications written for Windows thrived while non-Windows apps eventually died on the vine. It was Windows 3.0 that made Word and Excel the dominant apps in their spaces, beating out WordPerfect, 1-2-3, and other entrenched DOS-compatible competitors.
Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1, released in 1992, was more than a simple point upgrade. Version 3.1 not only included the requisite bug fixes, it was the first version of Windows to display TrueType scalable fonts—which turned Windows into a serious platform for desktop publishing. Also new to Windows 3.1 were screensavers and drag-and-drop operation.
Windows for Workgroups
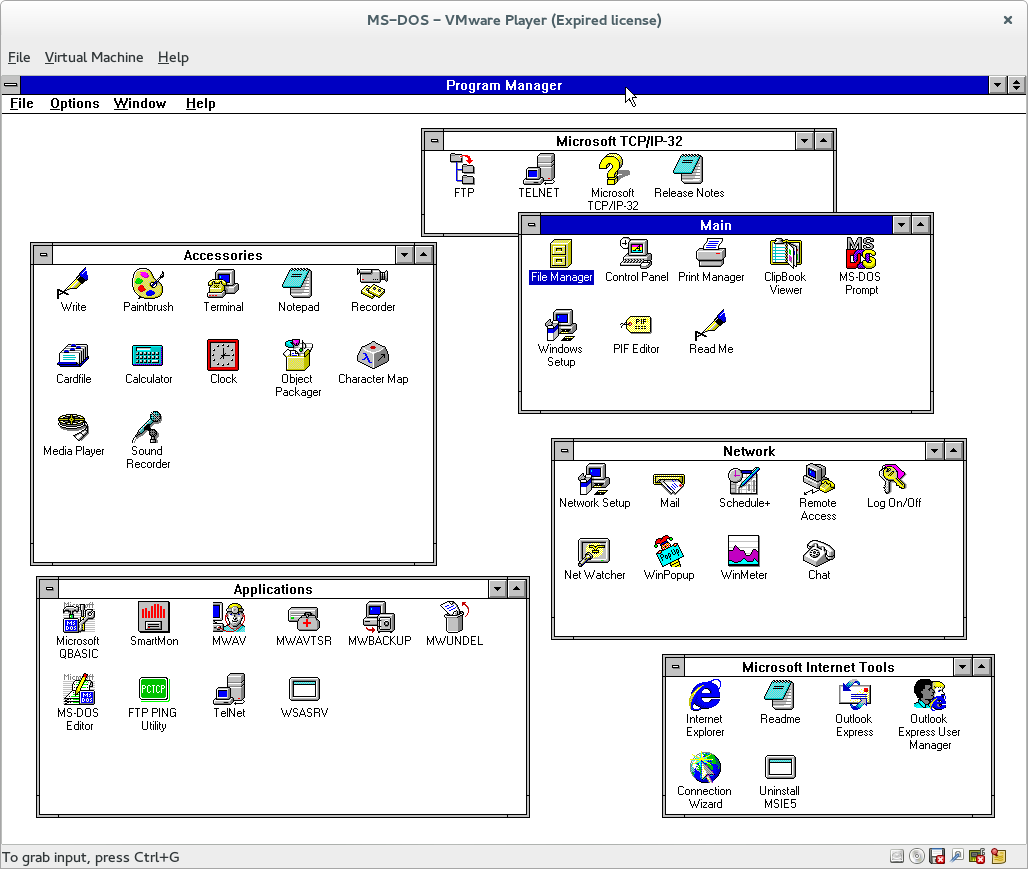
Also released in 1992 was Windows for Workgroups (WFW), the first networkable version for Windows. Originally developed as an add-on for Windows 3.0, WFW added the necessary drivers and protocols (including TCP/IP) for peer-to-peer networking. This made WFW the first version of Windows suitable for a corporate environment.
Figure 6 Windows for Workgroups—the first networkable version of Windows
With WFW, Windows releases split into two paths: The consumer path, designed for use on single PCs, represented by Windows 3.1 and the upcoming Windows 95, and the corporate path, designed for use on multiple networked PCs, represented by WFW and the upcoming Windows NT.
Related Resources
- Book $141.65
- Book $67.99
What Is My Workgroup Password
- Book $19.99